EDACafe Editorial Roberto Frazzoli
Roberto Frazzoli is a contributing editor to EDACafe. His interests as a technology journalist focus on the semiconductor ecosystem in all its aspects. Roberto started covering electronics in 1987. His weekly contribution to EDACafe started in early 2019. Smartphone upturn; Synopsys revenues; Amkor in Arizona; smaller AC/DC adapters; 22.9 Pbits/s on a fiberDecember 4th, 2023 by Roberto Frazzoli
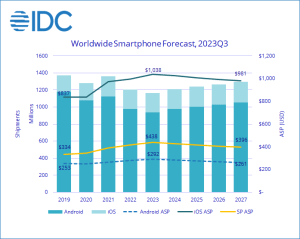
Let’s start this week’s news roundup with a “chip war” update which does not concern China. The Biden administration has reportedly forced a Saudi venture capital firm to sell its shares in Silicon Valley AI chip startup Rain Neuromorphics. According to Reuters, the move follows other actions the US has taken to slow AI development in the Middle East. Smartphone market is set for an upturn According to International Data Corporation (IDC), the drop in smartphone sales is finally over: the market research firm expects worldwide smartphone shipments to grow 7.3% year-over-year in the fourth quarter of 2023. The market recovery will continue in 2024 with 3.8% growth expected, followed by low single-digit growth for the rest of the forecast period, resulting in a five-year compound annual growth rate of 1.4%. According to IDC, the smartphone sector is entering the new era of low single-digit growth and lengthened refresh cycles, as the market is maturing. While the total available market will remain below pre-pandemic shipment levels throughout the forecast, average selling prices and market value will remain significantly higher than before. Synopsys 2023 revenues Synopsys has reported results for its fourth quarter and fiscal year 2023. Revenue for the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2023 was $1.599 billion, compared to $1.284 billion for the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2022. Revenue for fiscal year 2023 was $5.843 billion, an increase of approximately 15% from $5.082 billion in fiscal year 2022.
Amkor to build an advanced packaging and test facility in Arizona Amkor, a provider of semiconductor packaging and test services, has announced its plan to build an advanced packaging and test facility in Peoria, Arizona. By the time of full project completion, Amkor projects to invest approximately $2 billion and employ approximately 2,000 people at the new facility. Amkor worked closely with Apple on the strategic vision and initial manufacturing capability of the Peoria facility, which will package and test chips produced for Apple at the nearby TSMC fab. When the new facility opens, Apple will be its first and largest customer. To support this project, Amkor has applied for funding from the CHIPS and Science Act. AWS’ new chips Amazon Web Services has announced the next generation of two AWS-designed chip families: Graviton4 and Trainium2. According to the company, Graviton4 (based on Arm Neoverse) provides up to 30% better compute performance, 50% more cores, and 75% more memory bandwidth than current generation Graviton3 processors. Trainium2 is designed to deliver up to 4x faster training than first generation Trainium chips and will be able to be deployed in EC2 UltraClusters of up to 100,000 chips, making it possible to train foundation models (FMs) and large language models (LLMs) in a fraction of the time, while improving energy efficiency up to 2x. Broadcom’s new switch with on-chip neural network Broadcom has introduced what it claims is the industry’s first network switch with on-chip neural network: the new, software-programmable Trident 5-X12 chip. The integrated neural-network inference engine, called NetGNT (Networking General-purpose Neural-network Traffic-analyzer), can be trained to look for different types of traffic patterns that span the entire chip and can, for example, invoke congestion-control techniques to avoid degraded network performance. Speaking of Broadcom, the company will reportedly lay off about 1,300 VMware employees in California following its acquisition of the cloud-computing firm. Microchip’s new MCUs with Programming and Debugging Interface Disable feature The new PIC18-Q24 family of microcontrollers from Microchip introduces the Programming and Debugging Interface Disable (PDID) feature to counter the threat of maliciously reprogramming a device in an embedded system. When enabled, this enhanced code protection feature is designed to lock out access to the programming/debugging interface and block unauthorized attempts to read, modify or erase firmware. The PIC18-Q24 MCUs also feature Multi-Voltage I/O (MVIO). This solution eliminates the need for external level shifters and allows the MCUs to interface with digital inputs or outputs at different operating voltages. Renesas’ Risc-V-based 32-bit CPU Renesas has designed and tested a 32-bit CPU core based on the open-standard Risc-V instruction set architecture. Renesas claims to be among the first in the industry to independently develop a CPU core for the 32-bit general-purpose Risc-V market. As the company highlighted in a press release, while many MCU providers have recently created joint investment alliances to accelerate their development of Risc-V products, Renesas has already developed a new Risc-V core on its own. Details about the new Risc-V-based CPU can be found in this Renesas blog post. Texas Instruments’ low-power gallium nitride FETs Texas Instruments has expanded its low-power gallium nitride FET portfolio, designed to help improve power density, maximize system efficiency, and shrink the size of AC/DC consumer power electronics and industrial systems. According to TI, the new devices help designers reduce the solution size of a typical 67-W power adapter by as much as 50% compared to silicon-based solutions. Additionally, the new GaN FETs with integrated gate drivers offers an integrated current sensing functionality, eliminating the need for an external shunt resistor. According to TI, this also reduces associated power losses by as much as 94% when compared to traditional current-sensing circuits used with discrete GaN and silicon FETs. A technical article on this topic is available here. 22.9 petabits per second on a single optical fiber Researchers from Japan’s National Institute of Information and Communications Technology, in collaboration with the Eindhoven University of Technology (Netherlands) and University of L’Aquila (Italy) have demonstrated a record-breaking data-rate of 22.9 petabits per second using only a single optical fiber, which is more than double the institute’s previous world record of 10.66 petabits per second. In this work, researchers succeeded in combining the latest research technologies such as large-scale Space Division Multiplexing (SDM) and multi-band Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM), to demonstrate a path to future ultra-large capacity optical communication networks. Further reading A press release from market research firm Trendforce includes an overview of the different technologies used to produce ultra-thin glass and the respective players. Being flexible, ultra-thin glass is used to build displays for foldable phones. |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
|||||