EDACafe Editorial Roberto Frazzoli
Roberto Frazzoli is a contributing editor to EDACafe. His interests as a technology journalist focus on the semiconductor ecosystem in all its aspects. Roberto started covering electronics in 1987. His weekly contribution to EDACafe started in early 2019. Major stories this week: RISC-V; autonomous vehicles; AI events; Ge-based devices; etc.June 14th, 2019 by Roberto Frazzoli
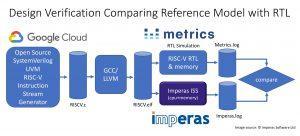
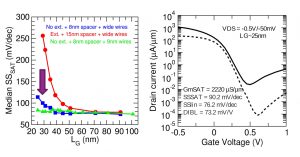
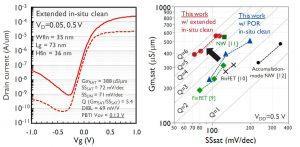
The RISC-V Workshop held in Zurich, Switzerland, from June 11th to 13th brought several announcements related to the popular open-source ISA; more news concern partnerships in the DMS and autonomous vehicle area. This week and the next, events are making Long Beach the capital of artificial intelligence; meanwhile, research institutes and universities keep studying semiconductor technology and new materials. RISC-V ecosystem expanding Right after crossing the 100-design win threshold, SiFive has announced it raised $65.4 million in a Series D round from a group of investors that now includes Qualcomm Ventures. Another aspect of RISC-V growing traction is the expansion of its ecosystem. Andes Technology has just introduced its RISC-V FreeStart program, promising “an easy and fast way” to build a SoC based on the commercial-grade RISC-V CPU core N22, available for free download. According to Andes, SoC designers using the N22 can skip the verification tasks required by open source RISC-V CPUs, which offer limited features and lack documentation. Supporting designers who plan to use RISC-V is also the goal of the newly formed OpenHW Group, a not-for-profit global organization aiming to boost the adoption of open-source processors. OpenHW Group will pursue this missione by providing a platform for collaboration, creating a focal point for ecosystem development, and offering open-source IP for processor cores. As an example, for RISC-V-based processors, the organization is introducing the CORE-V family of cores, which offers a manufacturability assurance. Inaugural OpenHW sponsors include Alibaba, Bluespec, CMC Microsystems, Embecosm, ETH Zurich (university), GreenWaves, Imperas, Metrics, Mythic AI, NXP, Onespin, Silicon Labs and Thales. Verification of RISC-V cores such as the CORE-V family from the OpenHW Group is among the applications of the new Design Verification framework being developed by UK-based Imperas and Canada-based Metrics, relying on Imperas commercial simulation technology combined with Metrics’ cloud-based verification platform. The framework uses Google’s open source SystemVerilog UVM-based Instruction Stream Generator. According to Imperas, until yesterday the extensive functional design verification effort of RISC-V implementations has not been addressed; now, the new framework makes industry best practices available to both commercial and open source RISC-V cores. Imperas has also announced the delivery of its updated simulator for the RISC-V Vector and Bit Manipulation Extensions to lead customers. In addition, the ratified RISC-V Specification is now available in the free RISC-V Open Virtual Platform Simulator (riscvOVPsim) as a reference Instruction Set Simulator (ISS). Another proposal comes from UK-based Axiomise, that has made available a RISC-V formal proof kit that offers exhaustive formal verification of RISC-V CPU designs against the RISC-V ISA. According to the company, the kit is easy to set up and requires neither formal expertise nor modifications to the designs. AV and driver monitoring partnerships Partnerships involving specialized companies are contributing to shape up the future value chain of autonomous vehicles. Fiat Chrysler US and Aurora have signed a memorandum of understanding for a partnership to develop and deploy self-driving commercial vehicles. Founded in 2017 by experts Chris Urmson, Sterling Anderson, and Drew Bagnell, Aurora has offices and tests its vehicles in Palo Alto, San Francisco and Pittsburgh. Another partnership involves ANSYS and BMW, that are creating a simulation toolchain specifically targeted at developing autonomous vehicle technologies. ANSYS will assume exclusive rights to the simulation toolchain, for commercialization to a wider market. But until autonomous vehicles become a reality, keeping human drivers awake remains a priority: that’s where Driver Monitoring Systems (DMS) come into play, this week with two new partnerships. DriverSense DMS software from the Israeli company Eyesight Technologies is now available on Ambarella CVflow automotive SoCs, delivering a market-ready driver state, action, and recognition system for incorporation into vehicles by OEM and Tier-1 automotive manufacturers. The solution has been demonstrated during CES Asia, June 11-13, in Shanghai, China. And a collaboration aimed to developing driver monitoring systems has been announced by NXP and Momenta (Beijng, China). The initial solution will combine the architecture of NXP’s Open Vision Platform (S32V2) with Momenta’s deep learning software. The collaboration aims to optimize, compress and accelerate deep neural networks, so that they can run efficiently on an automotive-grade DMS embedded platform. Long Beach ML and vision events And automotive application are certainly included among the themes of the two consecutive AI-related events taking place in Long Beach, CA, at this time: the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) from June 9th through June 15th, and the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR) from June 16th to June 20th – the latter organized by the Computer Vision Foundation and IEEE Computer Society. Google participation in ICML is massive, with nearly 200 Googlers attending the conference to present publications and host workshops. Germanium devices, Li-ion capacitors With Germanium becoming a promising candidate for future process nodes, Belgium-based research institute Imec has reported improved performance for both Ge-based n-type FinFETs and Ge-based p-type gate-all-around (GAA) devices. For Ge n-type FinFETs, pre-gate stack process optimization dramatically improved reliability and performance, with 100 percent better positive bias temperature instability (PBTI) and improvement in GmSAT vs. SSSAT benchmark. For the Ge-based p-type GAA device, excellent short-channel control and performance were achieved with an improved extension-less junction scheme. According to Imec, the results confirm the potential of Ge-based CMOS transistors as high-performance solutions for the 3nm and beyond technology nodes. These researches have been presented at the 2019 Symposia on VLSI Technology and Circuits (June 9-14, Kyoto, Japan). Widespread availability of low-cost lithium-ion capacitors is now closer thanks to a joint research team from Institut des matériaux Jean Rouxel (CNRS/Université de Nantes, France) and Münster Electrochemical Energy Technology (University of Münster, Germany). The new solution, aiming to industrial production, facilitates the incorporation of lithium in the capacitors by using a combination of two additives instead of just one. Intel to acquire Barefoot Networks Let’s close with an acquisition announcement: Intel has signed an agreement to acquire Barefoot Networks, an emerging player in Ethernet switch silicon and software for use in the data center. Intel expects that Barefoot’s specialization in programmable and flexible solutions – both necessary to meet the performance and needs of the hyperscale cloud – will support its focus on end-to-end cloud networking and infrastructure. |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
|||||