EDACafe Editorial Roberto Frazzoli
Roberto Frazzoli is a contributing editor to EDACafe. His interests as a technology journalist focus on the semiconductor ecosystem in all its aspects. Roberto started covering electronics in 1987. His weekly contribution to EDACafe started in early 2019. Apple-Intel deal; Alibaba’s RISC-V chip; semiconductor forecasts; EDA updates; 2D transistorsAugust 5th, 2019 by Roberto Frazzoli
Two major announcements attracted general attention over the past couple of weeks; and many more interesting stories poured in from both industry and academia. Let’s take a look at some of them. Apple to acquire Intel’s smartphone modem business As widely reported by many media outlets, on July 25 Intel and Apple announced an agreement for Apple to acquire the majority of Intel’s smartphone modem business. Approximately 2,200 Intel employees will join Apple, along with intellectual property, equipment and leases. The transaction, valued at $1 billion, is expected to close in the fourth quarter of 2019, subject to regulatory approvals and other customary conditions. Consistent with Apple’s strategy, the deal will allow the Cupertino tech giant to gradually become independent from external suppliers on this key technology; Intel, on its part, declared last April the intention to exit the 5G smartphone modem business citing “no clear path to profitability.” Alibaba introducing its own RISC-V-based processor Dubbed Xuantie 910, the processor recently announced by Alibaba Group’s chip subsidiary, Pingtouge Semiconductor, is based on sixteen RISC-V cores and manufactured on a 12nm process. As reported by EETimes, Alibaba claims this to be the most powerful RISC-V based processor, achieving 7.1 Coremark/MHz at 2.5GHz clock. New features enabling this performance level include a 12-stage pipeline and the addition of fifty instructions. With this move, Alibaba joins the other so-called “hyperscalers” (Internet giants) that have already developed their own chips. Many Chinese media outlets, however, have interpreted this announcement in the context of current trade tensions, with China striving to be independent from US technologies.
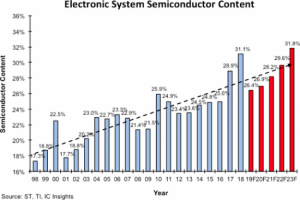
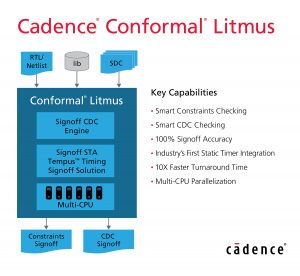
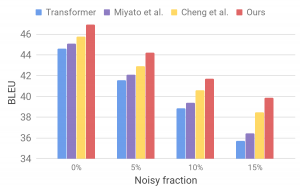
Semiconductor revenue to decline in 2019 According to Gartner, worldwide semiconductor revenue is forecast to total $429 billion in 2019, a decline of 9.6% from $475 billion in 2018. This is down from the previous quarter’s forecast of -3.4%. Among the factors impacting the market, Gartner cited a demand-driven oversupply in the DRAM market that will push pricing down 42.1% in 2019. Reduction of the average selling prices for DRAM and NAND flash was also cited by IC Insights to explain the expected decrease of the semiconductor content (in terms of value) in electronic systems. But the chip market is experiencing a slowdown in terms of quantities, too: according to SEMI, worldwide silicon wafer area shipments in the second quarter of 2019 totaled 2,983 million square inches, down 2.2 percent from the 3,051 million square inches shipped in the first quarter of the year and 5.6 percent lower than shipments during the same period in 2018. EDA updates Cadence has unveiled Conformal Litmus, a solution that provides constraints signoff and clock domain crossing signoff, reducing overall design cycle times and enhancing the quality of silicon in complex SoC designs. The company has also announced delivery of the Accellera Portable Test and Stimulus Specification (PSS) 1.0-compliant implementation of the Cadence Perspec System Methodology Library and methodology documentation. Synopsys and Ixia, a Keysight business, have announced a solution targeted at system validation of complex networking SoCs, based on Synopsys’ ZeBu and on Ixia's IxVerify. Microsoft and Globalfoundries have joined Silicon Integration Initiative’s OpenAccess Coalition, a group of semiconductor companies that support the OpenAccess design database application programming interface. The OpenAccess database provides EDA software tools with immediate design flow interoperability. Speech and language processing advancements Amazon Web Services (AWS) has announced two new features for Polly, its managed service that turns text into lifelike speech: Neural Text-To-Speech (NTTS), that increases naturalness and expressiveness, and the possibility to use a newscaster style, “a high-quality voice that sounds like what [listeners] might expect to hear on the TV or radio.” And language processing researchers gathered in Florence, Italy, from July 28th to August 2nd, to attend the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL). At this conference, Google presented an approach that uses generated adversarial examples to improve the stability of machine translation models against small perturbations in the input. Stability means avoiding that a subtle change to the input sentence causes the translation to become very different or even incorrect. Calcium fluoride insulator for ultrathin transistors Further downscaling of electronic devices could involve reducing thickness besides area, moving towards the so-called “2D transistors”. One of the hurdles on this path is making the gate insulation layer thin enough. According to a research team from TU Wien (Technische Universität, Vienna, Austria), the perfect material to replace silicon oxide in ultrathin FETs could be calcium fluoride. As the researchers explained in a paper published on Nature Electronics journal, “Typically used oxides such as SiO2, Al2O3 and HfO2 are (…) amorphous when scaled, and 2D hexagonal boron nitride exhibits excessive gate leakage currents”. Instead, “epitaxial calcium fluoride (CaF2), which can form a quasi van der Waals interface with 2D semiconductors, can serve as an ultrathin gate insulator for 2D devices”. The team has fabricated transistors with a crystalline CaF2 insulator of 2 nm thickness, “which corresponds to an equivalent oxide thickness of less than 1 nm”. These devices, they claim, “exhibit low leakage currents and competitive (…) performance characteristics, including subthreshold swings down to 90 mV dec−1, on/off current ratios up to 107 and a small hysteresis.” As reported by TU Wien website, the calcium fluoride layer was produced at the Ioffe Institute in St. Petersburg, Russia, where a member of the team is originally from. Partnerships and acquisitions Microsoft and OpenAI have partnered to accelerate breakthroughs in artificial general intelligence (the ability to perform any intelligent task, as opposed to AI that focuses on narrow specialized applications). Under the terms of the partnership agreement, Microsoft and OpenAI will jointly build new Azure AI supercomputing technologies; OpenAI will port its services to run on Microsoft Azure; and Microsoft will become OpenAI’s preferred partner for commercializing new AI technologies. Ford has acquired Quantum Signal (Saline, Michigan), a company specializing in robotic vehicles including those used for military applications. The US carmaker intends to use Quantum’s experience in real-time simulation and algorithm development – as well as robotics, sensing and perception technology – to advance its goal of launching a self-driving vehicle business. Upcoming events Lastly, let’s take a quick look at some upcoming events. Drive World with ESC will be taking place August 27 to 29 in Santa Clara, CA. The AI Hardware Summit returns at the Computer History Museum in Mountain View, CA, on September 17-18. TowerJazz will be holding its Technical Global Symposiums in Shanghai, China, on September 3rd; in Tokyo, Japan, on September 19th; and in Santa Clara, California, on November 20th. |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
|||||